Qi, Lingyan, Han Yin, Zhengxin Wang, Liuyi Dai, Liangtao Ye, Kejia Zhang, Mingzhu Guo, Haifeng Qi, and Jiacong Huang. 2025. “Constructing Time-Series Submerged Aquatic Vegetation by Integrating Process-Based Modeling and Satellite Images.” Ecological Modelling 504:111074. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2025.111074.
Abstract
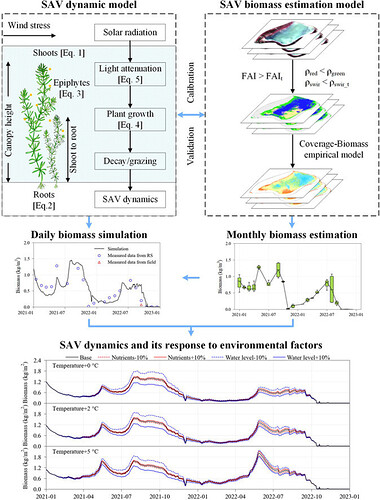
Submerged aquatic vegetation (SAV) plays a critical role in lake ecosystem health. However, quantifying the spatiotemporal patterns of SAV biomass remains challenging due to limited time-series data. To address this challenge, we integrated a process-based SAV dynamic model with a satellite-based SAV biomass estimation model to construct a time-series SAV dataset for Lake Zhanbei, a sub-lake within China’s largest freshwater lake, Lake Poyang. The integrated model effectively captured SAV biomass dynamics, with model performance of R2=0.60 and RMSE=0.24 kg/m2 compared to measured data. Results showed that SAV was more abundant near floodplain areas. A significant decline of SAV biomass was observed from 0.76 kg/m2 (2021) to 0.19 kg/m2 (2022), primarily due to a drop in the annual average water level from 14.1 m (2021) to 13.4 m (2022) caused by extreme drought. Water level was the most sensitive driver of SAV biomass, while temperature also had a notable impact under optimal water levels. Our scenario simulations revealed that global warming could enhance SAV growth, while nutrients had minimal effects. Compared with in-situ measurements from previous publications, the integrated model offers a cost-effective and high-resolution approach to study SAV dynamics, with potential applications in other lakes.